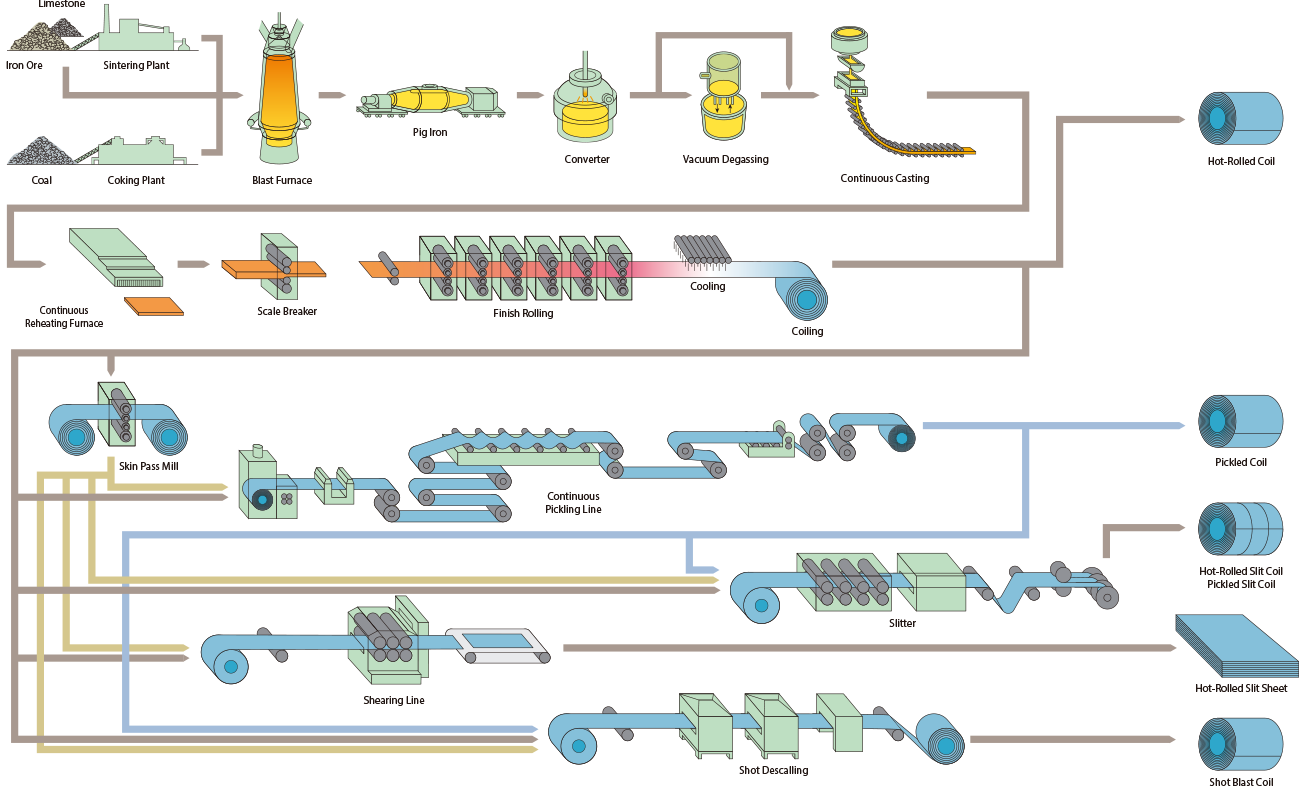
Hot-rolled steel coils are produced by rolling steel slabs at high temperatures (1,000–1,300C) into thin, flat strips, which are then coiled for ease of handling, storage, and transportation. This process enhances ductility and uniformity while reducing internal stress. The coils offer high strength, formability, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for applications in construction (structural components), automotive manufacturing (chassis parts), machinery, and pipe production. Common grades include low-carbon steel (e.g., Q235) and high-strength variants (e.g., Q345). Surface finishes like acid pickling or galvanization may be applied to improve corrosion resistance. After uncoiling, they are further processed into sheets, plates, or other shapes for fabrication, supporting industries requiring large-scale, durable materials.







Production Method and Uses of Hot-Rolled Steel Coils
Hot-rolled steel coils are manufactured by heating steel slabs to 1,000–1,300°C, rolling them into thin strips via roughing and finishing mills, and coiling for storage/transport. This process improves ductility and uniformity while reducing internal stress. After rolling, coils may undergo cooling (laminar or air) and surface treatments like acid pickling or galvanization. These coils are widely used in construction (structural beams, bridges), automotive (chassis, body parts), machinery, and pipe manufacturing. Their high strength, formability, and cost-effectiveness make them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring durability, such as shipbuilding, containers, and steel pipes. Common grades include low-carbon (e.g., Q235) and high-strength (e.g., Q345) steel, supporting industries globally.