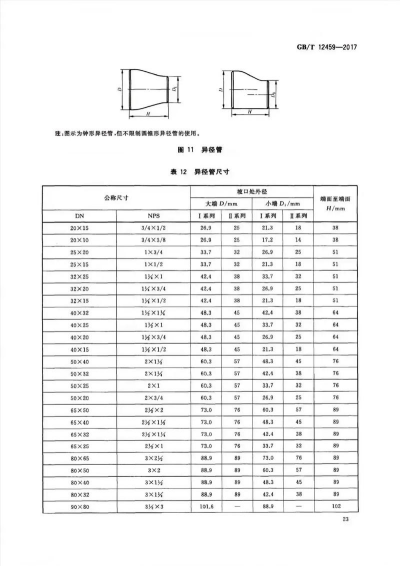
A carbon steel reducer is a pipe fitting connecting two pipes of different diameters, ensuring smooth fluid transition and reducing turbulence. Made from grades like Q235 or 20# steel, it comes in concentric (aligned centers) or eccentric (offset) types. Compliant with ASTM A234, ASME B16.9, or GB/T 12459 standards, it suits oil, chemical, and water systems. Produced via seamless or welded methods, it offers threaded or welded ends. Surface treatments (galvanizing, epoxy coating) enhance corrosion resistance. Rated for pressures up to Class 300, it withstands high temperatures and pressures, providing durability and cost-efficiency in industrial piping networks.






Advantages:
Cost-effective with high durability and resistance to high temperature/pressure.
Smooth fluid transition minimizes turbulence and energy loss.
Corrosion-resistant via galvanizing or epoxy coatings.
Flexible design options: concentric (aligned flow) or eccentric (prevent air pockets).
Applications:
Connects pipes of varying diameters in oil, gas, chemical, and water systems.
Optimizes flow distribution in industrial pipelines (e.g., throttling, expansion/contraction).
Used in high-pressure systems for energy efficiency and stability.
Supports maintenance in piping networks (e.g., eccentric reducers for drainage).